Hemm cassida del artichokeisem xjentifiku Cassida defloweredis an insect belonging to the order Coleopterafamilja Chrysomelidaesottofamilja Cassidinae. Huwa parasite of the artichoke very common in the southern and central regions and in the islands, but is present, albeit sporadically, also in the north. In case of heavy infestations, damage to artichoke crops they can be relevant, for this reason it is necessary to know how to recognize the parasite and to intervene promptly with biological defense.
In this article we see how to prevent and eliminate this animal that infests artichokes. But first let’s see how to recognize it.
Description of the artichoke cassida
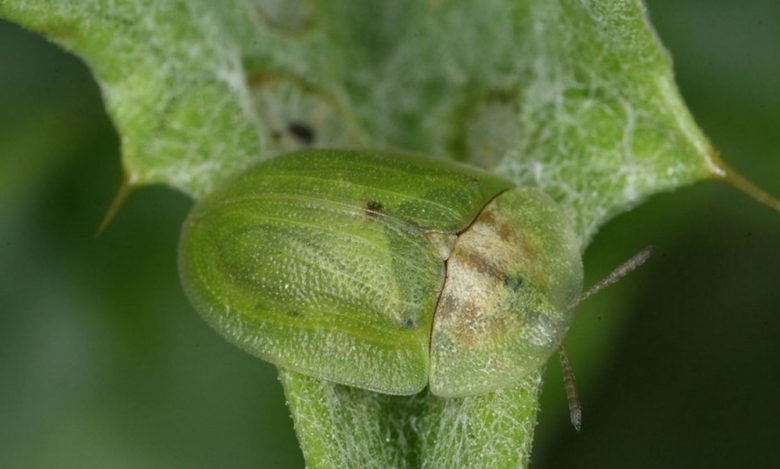

Hemm Cassida deflowered it is a small insect easily recognizable in the different stages of development. The adults measure 6-7 mm in length, are oval-convex, light green in color, with the head entirely hidden by the prothoracic shield. The legs are instead of a reddish color, with blackened femurs at the base. The elytra (wings) have parallel dotted lines.
Bajd
The eggs are yellowish in color and oval in shape. They are deposited in dense stratified ovoplates and covered by the blackish excrements of the females.
Larva
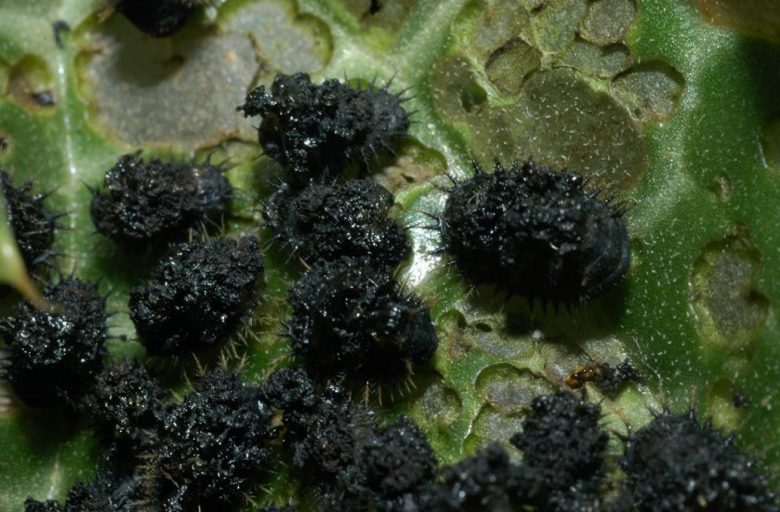

The larva of the artichoke cassida at full maturity measures 6-8 mm in length, the color is greenish-yellow with the head and legs not visible from above. The body is oval-elongated in shape, flattened on the back, with the margin decorated with small yellowish spines. At the end it is provided with a forked appendage on which the remains of the various moults and also the excrements accumulate. Therefore the larvae often appear completely black.
Pupae
The pupae of the artichoke cassida are green, with the distal part blackened. It has a semicircular prothoracic plate, with the posterior edge wider than the rest of the body, which is provided with lateral spines.
Plants attacked by the artichoke cassida
Hemm Cassida deflowered lives mainly at the expense of artichoke plantbut it can also infest spontaneous and cultivated thistles, the tussilago farfara u kultant il- pitravi.
Damage to plants
The damage to artichoke plants is due to the adults and the larval stages of the cassida. The parasite feeds on the vegetation by eroding the flap, respecting the opposite epidermis which subsequently dries up and tears.
If the infestation of Cassida deflowered it is elevated, the affected leaves are strongly pitted and end up drying out completely, compromising the vegetative development of the plant. The damage is stronger on young plants than in mature artichokes.
Life cycle of the deflowered Cassida
The artichoke cassida overwinters at the adult stage, taking refuge at the base of the leaf ribs of the plants or in the surrounding soil. At the beginning of spring, the adults come out of the shelters and carry on the leaves. Oviposition begins from mid-April (May in the North). The eggs are laid on the underside of the leaves or at the bifurcation of the ribs, more rarely on the inflorescences and on the stems. As mentioned, the eggs are laid in dense stratified groups and masked with the blackish droppings. After about 15 days of incubation the larvae are born, which reach maturity in a month, after five moults. At the end of their evolution they pupate, fixing themselves under the leaves. The new adult cassis are ready after about a month of pupal life. Adults continue to feed on the leaves for a long time, until wintering. The insect therefore makes only one generation in a year.
Insetti antagonistiċi
In nature there they are useful insects which parasitize the ovature of the cassis of the artichoke, in particular: the chalcidid hymenoptera Foersterella flavipes and the Mimarid Hymenoptera Fulmekiella balteata.
How to prevent artichoke cassida
In a small garden with a few artichoke plants, the biological defense against this parasite can be above all mechanical. During the oviposition period, between April and May, the vegetation of the plants should be carefully inspected and the ovature (rather evident) removed manually.
Another manual removal technique, of larvae and adults, is to place newspaper sheets under the plants and then shake the leaves, collecting as many insects as possible.
In the autumn-winter period, the tillage of the soil around the plants limits the parasite’s chances of surviving the winter.
How to eliminate the artichoke cassida
On larger artichoke fields, mechanical defense against this parasite is impractical. There are two prodotti permessi fil-biedja organika which can be used to eliminate the artichoke casside.
L-ewwel hija l- beauveria bassianaa entomopathogenic fungus effective on both adults and larvae and that you find in the best agricultural shops.
Alternatively, products based on piretru naturalieasier to find (lo misjuba fi ħwienet speċjalizzati).






Ibda Thread ġdid